교과과정
- 교육목적
생태계 이용 기술, 인공 생태계 조성 기술, 생태계 복원 기술, 생태적으로 건전한 생물 수확 설계, 청정생산 기술 등 인간과 자연의 공존을 목적으로 자연환경을 이용하여 지속가능한 생태계를 설계하는 과학기술을 연구·교수하고 지구의 미래를 책임질 국제적 연구 인력의 양성
- 교육목표
-
- 자연환경을 이용하여 지속가능한 사회를 설계
- 비점오염원에 의한 하천생태 복원기술과 생태공학적 수질관리
- 에코시티 조성, 미생물 자원을 활용한 생태계 복원
- 생태계 가치평가, 시스템 분석 및 연안생태계 평가
- 습지, 식물을 활용한 오염정화 및 생태계 복원기술 연구
- 모델링을 통한 생태계 변화 예측 및 유해물질의 거동 연구
- 해조장, 해초장 복원기술 및 해양생태계 연구
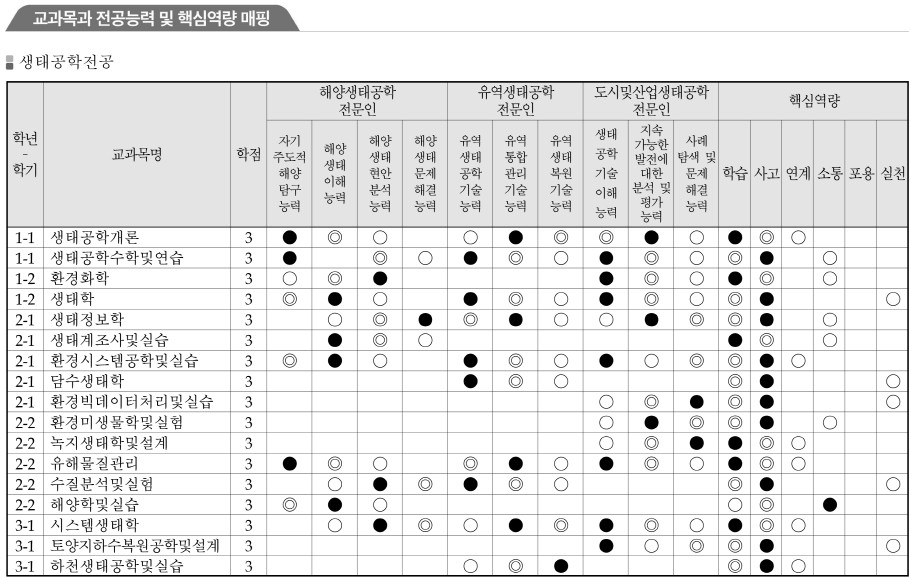
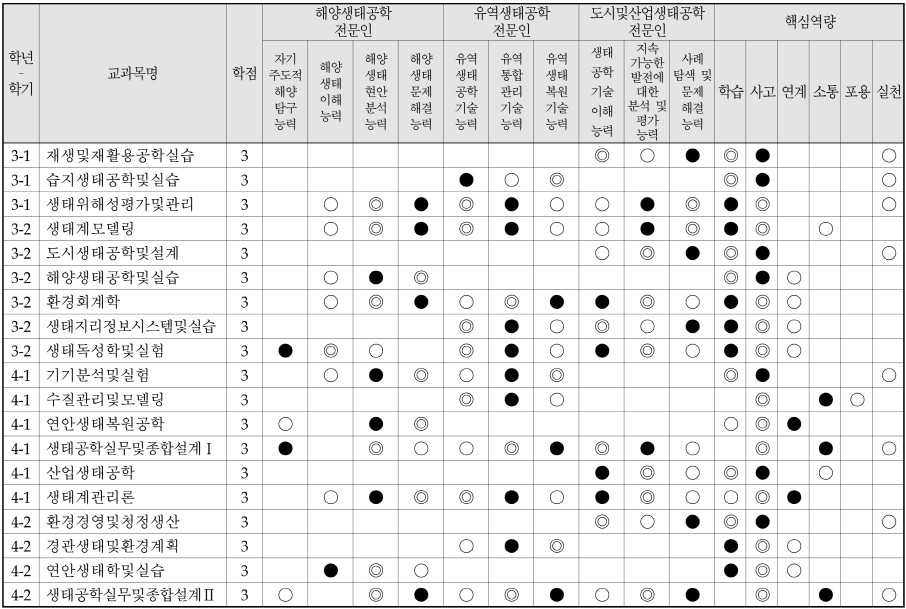
- 교과목과 전공능력 및 핵심역량 매핑
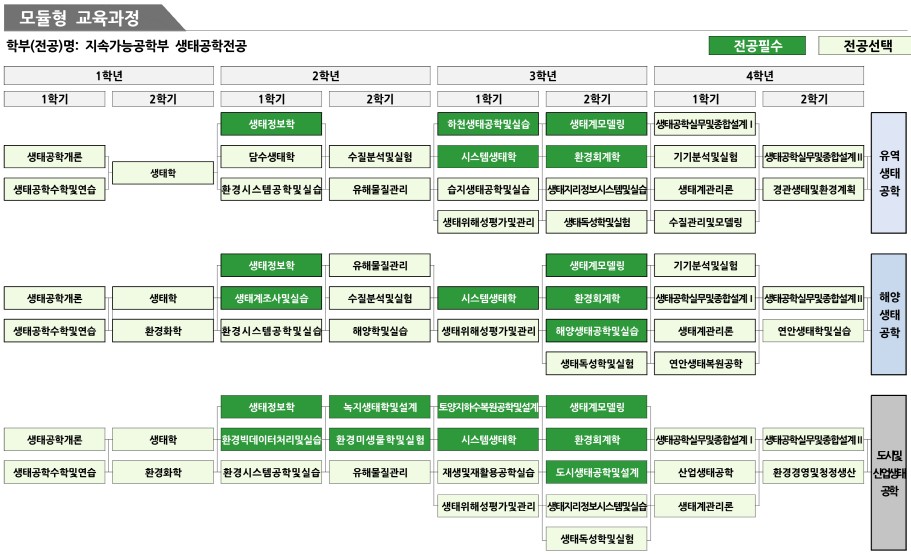
- 모둘형 교육과정
- 교과 요목
- 1학년 전공 교과목
[1학기]
1. 생태공학개론(Introduction to Ecological Engineering) : 화석연료에 의존하는 사후처리 중심의 기존 환경관리가 가지고 있는 한계를 극복하고, 생태계가 스스로 조직하는 능력을 이용해 인간과 자연이 공존하는 디자인을 찾고자 하는 학문인 생태공학은 자원고갈과 환경훼손으로 인류의 지속가능성이 위협받고 있는 지금 생태계 관리와 환경오염관리를 위한 새로운 시각과 방법론을 제공할 수 있는 학문이다. 이 과목에서는 생태공학의 개념과 원리를 이해하고, 생태공학의 다양한 적용 분야를 살펴본다.
2. 생태공학수학및연습(Mathematics for Ecological Engineer and Practice) : 생태공학 분야에 필요한 기본적인 수학 이론을 습득하고, 이를 바탕으로 자연계에서 발생하는 다양한 현상을 이해하며, 생태공학 교과에서 다루는 수학 문제를 컴퓨터 프로그램을 활용해 해석하고 적용할 수 있도록 한다.
[2학기]
3. 생태학(Ecology) : 생태계에서 일어나는 에너지와 물질의 흐름은 우리 삶의 근본 토대이다. 양적인 성장 위주의 경제발전을 통해 인류의 삶의 수준이 나아지기는 하였지만, 그 과정에서 경제발전의 토대인 생태계 훼손은 가속화하였다. 전 지구적인 자원고갈과 환경훼손이 인류의 지속가능성을 위협하고 있는 지금 인간 삶의 기본 토대인 생태계에 대한 이해는 아주 중요한 일이다. 이 과목에서는 인류의 지속가능한 발전과 관련하여 생태학이라는 학문이 어떤 역할을 할 수 있을 것인가에 대해, 생태학 정의, 생태계, 에너지와 물질 흐름, 생물다양성을 중심으로 공부한다.
4. 환경화학(Environmental Chemistry): 인간 활동에 따른 환경 문제 평가를 위한 화학적 기초를 학습하고, 화학물질이 생태계에 미치는 영향을 이해한다.
- 2학년 전공 교과목
[1학기]
5. 환경시스템공학및실습(Environmental System Engineering & Practices) : 이 과목에서는 대기, 강, 호수, 하구, 해양의 주요 성분과 이들의 분포에 영향을 미치는 환경적 특성에 대해 학습한다. 암석, 물, 대기, 생명을 구성하는 주요 성분이 어떻게 육지, 바다, 대기를 순환하는지 전 지구적 관점에서 통합적으로 이해하는 것이 중요하다. 인간 활동이 주요 성분의 지화학적 순환에 미치는 영향을 지구온난화, 산성비, 암석 풍화, 침식, 호수·하구 부영양화, 해양산성화 등을 중심으로 학습한다.
6. 생태계조사및실습(Ecosystem Survey and Monitoring) : 생태계를 이해하고, 보전하며, 이용하기 위하여 중요한 것은 생태계의 현황을 파악하는 것이다. 본 과목에서는 생태계의 구조와 상태를 파악하기 위한 조사방법과 조사자료를 분석할 수 있는 기술을 습득한다.
7. 생태정보학(Ecological Informatics) : 생태과정에 대한 전산학적, 수리학적 접근 방법을 학습하고 생태 자료의 유형화 및 분석, 적용에 관하여 이해한다.
8. 담수생태학(Fresh Water Ecology): 바다가 아닌 육지에 있는 물(하천, 호수 등)생태계를 연구하는 학문으로 이러한 담수생태계의 물리화학적 특성, 에너지와 물질 흐름, 생태계 구조와 기능에 대해 학습한다. 이를 바탕으로 부영양화, 녹조와 같은 담수생태계의 오염과 훼손에 어떻게 대처할 것인지 이해한다.
9. 환경빅데이터처리및실습(Big Data Processing and Practices): 파이썬 패키지 활용을 위한 기초이론과 실제 예제를 교수하고 이를 통해 빅데이터를 처리할 수 있는 능력을 배양한다.
[2학기]
10. 수질분석및실험(Water Quality Analysis and Laboratory) : 물의 이화학적 성질과 수질분석법의 기본원리를 이해시킨 후 실험을 통하여 수질관리에 필요한 중요항목의 수질분석법을 습득시킨다.
11. 해양학및실습(Oceanography and Practices) : 생물생산, 에너지자원공급, 기후조절과 같이 지구의 생명유지시스템에 아주 중요한 해양의 다양한 요소들을 전체 시스템의 관점에서 살펴보고, 이들 구성요소들이 서로 작용하는 원리를 파악함으로써 해양환경의 특성과 지속가능발전의 실현에서 해양환경의 중요성(인간과 바다의 상호작용)을 공부한다.
12. 환경미생물학및실험(Environmental Microbiology & Lab) : 미생물은 생태계를 구성하는 매우 중요한 요소로서 자연환경으로 유입되는 오염물질의 제어에 중요한 역할을 수행할 수 있다. 본 과목에서는 미생물의 기본 구조, 분류, 기능, 미생물 생태학에 대하여 이해하며 미생물이 다양한 환경오염문제에 어떻게 활용할 수 있는가를 공부한다.
13. 녹지생태학및설계(Green Space Ecology and Design) : 육상생태계의 주요 생산자인 식물과 그 서식 환경을 학습하고, 식물이 제공하는 다양한 생물서식처에 대한 이해를 바탕으로 생물의 서식처 특성을 파악한다. 이를 통해 인공지반 녹화 및 대체·복원 서식지의 설계, 조성, 관리 기술을 습득하고 실무에 적용할 수 있도록 한다.
14. 유해물질관리 (Hazardous Materials Management): 단기간 또는 장기노출로 생태계와 인체에 유해한 영향을 미치는 물질들에 대해 이해하며, 유해물질의 환경상 또는 인체 건강상의 위해를 예방 및 진단을 할 수 있는 전문 지식을 학습한다.
- 3학년 전공 교과목
[1학기]
15. 시스템생태학(Systems Ecology) : 생태계를 예로 들어 모든 시스템에 공통으로 나타나는 일반시스템의 개념을 소개하고 시스템생태학의 기본 원리에 대해 학습한다. 시스템의 구조와 기능을 간단하게 나타내는 방법을 배우고, 시스템의 네트워크 특성을 학습한다. 에너지시스템 다이어그램과 미니모델 시뮬레이션을 통해 복잡한 시스템을 이해할 수 있도록 한다.
16. 재생및재활용공학실습(Recycling and Reuse of Wastes and Practices) : 폐기물 관리를 위한 기초이론과 실습을 수행하고 환경친화적 산업구축을 위한 산업계의 재활용 활성화방안을 교수한다.
17. 생태위해성평가및관리(Ecological risk assessment and management) : 화학물질이 인체를 포함한 생태계에 미치는 위해성의 평가 및 관리방안을 제시한다.
18. 토양지하수복원공학및설계(Soil and Groundwater Remediation and Design) : 토양 및 지하수의 특성을 이해하고, 이들 매체에서 관련된 오염물질의 이동, 분배, 제거에 관련된 기작 들을 소개한다. 오염된 토양 및 지하수의 조사, 분석, 평가 및 해당 지역에서의 오염 확산 방지 및 정화 관련 기술들을 적용할 수 있도록 하며, 실제 오염지역에 정화 기술을 설계, 적용, 모니터링 할 수 있는 기술들에 대하여 소개한다.
19. 하천생태공학및실습(River Ecological Engineering & Practice) : 하천환경과 생물로 구성된 하천생태계를 이해하고, 하천생태계의 이용과 복원 및 조성에 대하여 실습한다.
20. 습지생태공학및실습(Wetland Ecological Engineering and Practices) : 습지의 중요성을 인식하고, 관련된 국제법 및 국내법의 현황을 학습한다. 또한 습지 관리에 필요한 조사, 분류, 기능 평가 방법을 익히며, 생지화학적 특성을 이해한다. 현장실습을 통해 습지의 기능을 파악하고, 이를 바탕으로 습지 복원 및 조성 기술을 실무에 적용할 수 있도록 한다.
[2학기]
21. 생태계모델링(Ecological Modelling) : 생태계에 대한 기본개념을 이해하고, 생태계내 구성원들의 동태를 수식화하여 시뮬레이션을 통한 미래예측과 이에 따른 관리방안을 제시한다.
22. 환경회계학(Environmental Accounting) : 생태계가 우리 경제의 진정한 부에 기여하는 가치를 평가하고자 하는 에머지 개념을 이해하고, 생태자원의 가치를 평가하는 방법을 학습한다. 이를 통해 에머지 개념을 이용한 환경회계 방법론이 생태계의 지속가능한 이용을 위한 정책의 수립과 이행, 평가에 어떻게 활용될 수 있는지 학습한다.
23. 생태지리정보시스템및실습(Ecological Geographic Information System and Practice) : 생태 분야에서 다양하게 활용되고 있는 원격탐사(Remote Sensing)와 지리정보시스템(GIS: Geographic Information System)에 대해 이론적으로 학습하고, 관련 프로그램의 활용 방법을 익힌다. 이를 통해 생태계의 구조와 기능을 이해하고, 생태계의 공간적 분포와 변화 양상을 분석할 수 있는 능력을 기른다. 나아가 이러한 기술을 생태계의 관리, 복원, 평가 등 다양한 실무 분야에 적용함으로써, 공간 기반 생태 정보를 효과적으로 수집·해석·활용할 수 있도록 한다.
24. 해양생태공학및실습(Marine Ecological Engineering & Practice) : 해양환경과 생물로 구성된 해양생태계를 이해하고 해양생태계의 이용과 복원 및 조성에 대하여 강의한다.
25. 도시생태공학및설계(Urban Ecological Engineering) : 기존 도시의 모습에서 생태공학적인 개념이 도입되는 도시로의 전환을 위한 기초적 개념을 교수한다.
26. 생태독성학및실험(Ecotoxicology and Lab) : 생태계의 기능과 구조, 그리고 오염물질 사이에서의 상호작용에 대해 이해하며, 오염물질의 다양한 노출경로와 영향에 대해 학습한다. 이를 기반으로 화학물질에 대한 지속가능성에 대해 고민하는 능력을 함양하며, 생태독성학적 이해와 과학적 근거를 제시할 수 있도록 한다.
- 4학년 전공 교과목
[1학기]
27. 기기분석및실험(Instrumental Analysis & Lab) : 물질의 성분과 구조의 정성적, 정량적 분석을 위한 각종 화학분석용 기기들의 기본원리를 이해하고, 사용법 그리고 응용에 관한 지식을 습득한다.
28. 산업생태공학(Industry Ecological Engineering) : 산업의 생태학적 관리의 측면에서 생태산업단지조성을 위한 개념, 방법론 교수 후 팀 별 프로젝트를 실시하고, 산업현장에서 작업자 보호를 위한 산업 환경에 대하여 교수한다.
29. 연안생태복원공학(Marine Restoration Engineering) : 연안 생태계를 구성하는 시스템과 기능을 이해하고, 해양생태계의 지속 가능한 이용과 복원 및 조서에 관한 전반적인 내용을 학습할 수 있도록 강의한다.
30. 생태공학실무및종합설계Ⅰ(Ecological Engineering Practice Ⅰ) : 지속 가능한 사회를 불가능하게 하는 현재 상황을 인식하고 왜 그런지 문제점을 분석하여 이를 개선할 수 있는 방법, 절차, 도구 등 생태 공학 원리를 이용해 해결책 또는 대안을 제시하기 위한 연구를 진행 한다. 또한, 생태공학과 전공 과정에서 배운 지식과 방법을 실무 현장에 적용하는 훈련을 통해 연구 및 문제해결 역량 및 취·창업 역량을 강화도록 하며, 팀 과제를 수행함으로써 협동심과 배려심을 키우고 긍정적인 토론 문화에 참여하여 학생 스스로 연구 및 문제 해결 능력을 배양하도록 한다.
31. 생태계관리론(Ecosystem Management) : 다양한 재화와 서비스를 생산하는 생태계는 인류 생존의 기반이다. 성장 위주의 경제 논리에 치우친 개발 정책으로 감소하고 있는 생태계의 생산성과 다양성을 확보하는 것은 인류의 지속가능발전에 필수적인 요소이다. 이 과목에서는 이러한 생태계를 시스템 관점에서 어떻게 관리할 것인지 생태계 관리의 기본 개념에 대한 학습을 바탕으로 생태계 관리 성공 및 실패 사례를 통해 현장에서 생태계 관리가 어떻게 이루어져야 하는지 배운다.
32. 수질관리및모델링(Water Quality Management & Modeling) : 생태계의 기능과 구조, 그리고 오염물질 사이에서의 상호작용에 대해 이해하며, 오염물질의 다양한 노출경로와 영향에 대해 학습한다. 이를 기반으로 화학물질에 대한 지속가능성에 대해 고민하는 능력을 함양하며, 생태독성학적 이해와 과학적 근거를 제시할 수 있도록 한다.
[2학기]
33. 환경경영및청정생산(Environmental Management and Cleaner Production) : ISO14000을 중심으로 한 전과정평가 및 환경경영체제, 청정생산기술의 개념 및 사례에 대하여 교수한다.
34. 경관생태및환경계획(Landscape Ecology and Environmental Planning) : 지속가능한 발전의 관점에서 환경계획의 중요성을 이해하고, 환경계획, 경관생태 등의 기초 개념을 학습한다. 이를 바탕으로 국토 차원 또는 지역 단위에서 환경계획이 어떻게 적용되는지를 살펴보며, 주민 참여와 환경영향평가 등 관련 제도에 대한 이해를 통해 환경계획의 수립, 평가, 조정 및 활용에 필요한 전문 지식을 갖출 수 있도록 한다.
35. 연안생태학및실습(Coastal Ecology and Practices) : 하구, 연안습지, 대륙붕 등 연안생태계의 환경특성과 생태계의 기능 및 구조를 전체 시스템의 관점에서 이해하고, 인간의 사회경제활동에서 연안생태계가 차지하는 중요성과 연안생태계를 이용하는 경제활동이 연안생태계의 생물과 생산성에 미치는 영향에 대해 학습한다.
36. 생태공학실무및종합설계Ⅱ(Ecological Engineering Practice Ⅱ) : 지속 가능한 사회를 불가능하게 하는 현재 상황을 인식하고 왜 그런지 문제점을 분석하여 이를 개선할 수 있는 방법, 절차, 도구 등 생태 공학 원리를 이용해 해결책 또는 대안을 제시하기 위한 연구를 진행 한다. 또한, 생태공학과 전공 과정에서 배운 지식과 방법을 실무 현장에 적용하는 훈련을 통해 연구 및 문제해결 역량 및 취·창업 역량을 강화도록 하며, 팀 과제를 수행함으로써 협동심과 배려심을 키우고 긍정적인 토론 문화에 참여하여 학생 스스로 연구 및 문제 해결 능력을 배양하도록 한다.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Major Subjects in Ecological Engineering course for freshman
[First Semester]
1. Introduction to Ecological Engineering:
Ecological engineering is a discipline to overcome traditional environmental and resource management based on fossil fuels and investigate designs for humanity and nature to coexist by relying on the self-organizing capability of ecosystems. It can provide new perspectives and sustainable ways to manage our invaluable ecosystems and their resources. This class introduces the basic concepts and principles of ecological engineering and its applications to the real world problems.
2. Mathematics for Ecological Engineer and Practice:
Students will acquire fundamental mathematical theories required in the field of ecological engineering. Based on this knowledge, they will develop an understanding of various natural phenomena and learn to interpret and apply mathematical problems used in ecological engineering courses through computer programming.
[Second Semester]
3. Ecology:
Ecology is an important field of study that investigates the interactions of organisms and surrounding physical and chemical environments. It provides essential information on what we have to do to balance utilization of resources supplied by ecosystems and preservation of ecological systems for the benefit of both. This course introduces the definition of ecology, ecosystems, energy flow and material cycles, and biodiversity that will help students understand the biophysical basis and sustainability of our economy.
4. Environmental Chemistry:
This course is to instruct the basic principles of chemistry for evaluating environmental problems according to human activities. Also it covers the effect of the various chemicals on the ecosystem.
- Major Subjects in Ecological Engineering course for Sophomore
[First Semester]
5. Environmental System Engineering & Practices:
In this class, students learn principal constituents and environmental characteristics of air, rivers, lakes, estuaries, and oceans. It is important for them to understand how the principal constituents of rocks, water, air, and life circulate through the land, the sea, and the air in terms of global geochemical cycles. This class will guide the students to understand how human activities affect the geochemical cycles of the principal constituents, focusing on environmental problems such as global warming, acid rain, rock weathering, erosion, eutrophication of lakes and estuaries, and ocean acidification.
6. Ecosystem Survey and Monitoring:
This course is to provide the scientific information to the present state and the latest technique for ecosystem survey and monitoring. By working together toward these solutions, we can ensure the sustainability of these coastal resources and allow for ecological development that will enhance the well-being of the marine ecosystem function and ability.
7. Ecological Informatics:
This course is to understand the basic principles of the mathematical and computational approach to ecological processes.
8. Fresh Water Ecology:
Limnology is a scientific field that studies fresh or saline waters contained within continental boundaries. This course introduces physical and chemical environments in those waters, energy and material flows, and ecosystem structures and functions to help students understand the appropriate ways pollution and ecosystem degradation are tackled.
9. Big Data Processing and Practices:
Teach theoretical lectures and practices of Python, Pandas, and numpy programs by learning the ability to read and process various forms of data.
[Second Semester]
10. Water Quality Analysis and Laboratory:
This course is to understand the principles of water quality analysis. It covers the training of analytical skill for inorganic ion, organic compound, plant nutrients, heavy metals and toxic chemical substances in the aquatic environments.
11. Oceanography and Practices:
This course introduces diverse components of seas and oceans in a systems perspective, regarding biological production, energy and resource supply, climate control and so on. By understanding how these components interact, students will learn how important the oceanic systems are for the human society and its economic activities.
12. Environmental Microbiology & Lab:
To understand and experiment basic and principles relating to environmental microbiology.
13. Green Space Ecology and Design:
Students will study plants as the primary producers of terrestrial ecosystems and their habitats, gaining an understanding of the diverse biological habitats they support. Building on this knowledge, they will learn to identify habitat characteristics and develop practical skills in designing, creating, and managing artificial green surfaces and replacement or restored habitats.
14. Hazardous Materials Management:
This course aims to understand substances that impose negative effects on the ecosystem and human health through either short-term or long-term exposure. Furthermore, students will acquire specialized knowledge pertinent to the prevention and diagnosis of the environmental or human health risks posed by hazardous materials.
- Major Subjects in Ecological Engineering course for Junior
[First Semester]
15. Systems Ecology:
Starting with ecosystems as examples, introduce general systems concepts common to all systems. To introduce principles of systems ecology and environmental science. To learn how to simplify systems by aggregation. To use networks to synthesize by combining mechanisms. To develop expanded mental capacity to understand complex systems through energy systems diagramming and minimodel simulation.
16. Recycling and Reuse of Wastes and Practices:
To understand important solid waste treatment processes and principles relating to environmentally important technologies for reuse and recycling.
17. Ecological risk assessment and management:
This course is to instruct the basic principles of the chemical exposure assessment, health risk assessment and ecological risk assessment. Also it covers risk management and communication.
18. Soil and Groundwater Remediation and Design:
Students will study the properties of soil and groundwater and learn the mechanisms governing contaminant transport, distribution, and remediation. They will acquire skills in site investigation, analysis, and evaluation, and apply pollution control and cleanup technologies. Practical training will enable them to design, implement, and monitor remediation strategies in real-world contaminated environments.
19. River Ecological Engineering & Practice:
Understanding river ecosystem which consists of the river environment and the living organisms, and practicing the sustainable use, the restoration and creation of the river ecosystem.
20. Wetland Ecological Engineering and Practices:
Students will recognize the ecological importance of wetlands and examine relevant international and domestic legal frameworks. They will learn techniques for wetland assessment—including investigation, classification, and functional evaluation—and gain an understanding of biogeochemical processes. Fieldwork will support the practical application of wetland restoration and creation methods.
[Second Semester]
21. Ecological Modelling:
A comprehensive understanding wetland management and wetland ecology. Topics on valuation, classification, investigation, management, restoration, and treatment of wetlands will be discussed. Field study of wetland in south Korea and pilot scale laboratory study of wetland for water treatment will be conducted.
22. Environmental Accounting:
This class introduces the emergy accounting for the evaluation of ecological resources and their economic uses. Students will learn the energy systems language to identify sources and pathways of systems to be evaluated and how the emergy accounting contributes to policies on ecosystems and their resources.
23. Ecological Geographic Information System and Practice:
Students will learn the theoretical principles of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), widely applied in ecological research and practice. They will gain proficiency in using relevant software tools to analyze spatial patterns and changes in ecosystems. These skills will be applied to real-world tasks such as ecosystem management, restoration, and evaluation, supporting the effective use of spatial ecological data.
24. Marine Ecological Engineering & Practice:
This course is the study of marine ecosystem consists of marine environments and organisms. Recently, devastation of the coastal areas causing barren grounds, thermal pollution, organic compounds, and global warming is increasing in many parts of the world resulting in the loss of natural population of many marine organisms. Furthermore, depletion of marine resources became depleted. In order to overcome these phenomena and bring increase marine biological resources, marine ecological engineering has become an important and popular technique in the coastal areas for the enhancement of marine resources.
25. Urban Ecological Engineering:
This course is to know the concepts of urban ecology and design ecological urban by evaluating of environmental and ecological problems on the urban scale.
26. Ecotoxicology and Lab:
This course aims to understand interactions between the function and structure of ecosystems and various pollutants. Students will systematically study the diverse exposure routes and the resulting effects of these pollutants. Based on this foundational knowledge, students will cultivate the capacity to critically contemplate the sustainability of chemical substances uses and will be equipped to present sound ecotoxicological comprehension.
- Major Subjects in Ecological Engineering course for Senior
[First Semester]
27. Instrumental Analysis & Lab:
This course is to instruct the basic principles of molecular spectrometry, atomic absorption spectrometry, chromatography and mass spectrometry. Also it covers the treatment of environmental sample and the analysis of environmental sample.
The purpose of this course is to introduce concepts such as sustainable development and the industrial ecology infrastructure, and an industrial ecology intellectual framework.
29. Marine Restoration Engineering:
This course is to provide the highest quality scientific information to coastal conservation and restoration for marine environments and organisms. To help achieve this, marine restoration engineering lecture a program of developing documents that would synthesize information on issues that were of high priority to coastal condition. As a contribution to the marine condition, this course provides a critical synthesis of the methods for planning, planting, monitoring, and evaluating conservation and restoration.
30. Ecological Engineering Practice Ⅰ:
Conduct research to recognize the current situation that makes it impossible for a sustainable society, analyze the problems, and present solutions or alternatives to use ecological engineering principles and provide methods, procedures, and tools to improve them. Also, The research, problem-solving and job start-up competencies are strengthened through training that applies the knowledge and methods learned in the major course of ecological engineering to the practical field. By carrying out team tasks, students are encouraged to develop a sense of cooperation and consideration, become familiar with a positive discussion culture, research and develop problem-solving skills independently.
31. Ecosystem Management:
Ecosystems that produce various goods and services are the fundamental basis of human survival. It is very important for the sustainability of our socioeconomic activities to maintain and restore the productivity and diversity of ecosystems that have been greatly impacted by the growth-oriented economic policies over the past decades. This course introduces the concept of ecosystem management and analyze cases of success and failure that employed ecosystem management approaches. Students will also discuss how to manage ecosystem on a systems perspective.
32. Water Quality Management & Modeling:
This course aims to understand interactions between the function and structure of ecosystems and various pollutants. Students will systematically study the diverse exposure routes and the resulting effects of these pollutants. Based on this foundational knowledge, students will cultivate the capacity to critically contemplate the sustainability of chemical substances uses and will be equipped to present sound ecotoxicological comprehension.
[Second Semester]
33. Environmental Management and Cleaner Production:
The purpose of this course is to know the concepts of ISO 14000 to shift industry to environmentally friendly structure and sustainable industrial development.
34. Landscape Ecology and Environmental Planning:
Students will explore the significance of environmental planning within the framework of sustainable development, learning core concepts such as environmental capacity, planning strategies, and landscape ecology. They will examine applications of environmental planning at national and regional scales, and gain insight into related systems including public participation and environmental impact assessment. This course equips students with the professional knowledge required to formulate, evaluate, adjust, and implement environmental planning in practice.
35. Coastal Ecology and Practices:
Coastal ecology is the study of real-world features and phenomena. The seas around Korea and many territories encompass every known marine environment found globally (except for deep-sea hydrothermal vents), and we have a great diversity of habitats and endemic species. It is not surprising, therefore, that Coastal ecology have contributed much newknowledge to many facets of marine sciences. In this course, we try to put those contributions into the wider context of global marine, and more general, ecology.
36. Ecological Engineering Practice Ⅱ:
Conduct research to recognize the current situation that makes it impossible for a sustainable society, analyze the problems, and present solutions or alternatives to use ecological engineering principles and provide methods, procedures, and tools to improve them. Also, The research, problem-solving and job start-up competencies are strengthened through training that applies the knowledge and methods learned in the major course of ecological engineering to the practical field. By carrying out team tasks, students are encouraged to develop a sense of cooperation and consideration, become familiar with a positive discussion culture, research and develop problem-solving skills independently.